With the added availability of Emcare, we’ve been asked by our library members which database they should use when searching for nursing and allied health literature searches. Below is a summary and comparison of the two to help you decide.
CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing & Allied Health) provides indexing of the top nursing and allied health literature available. The literature covers a wide range of topics including nursing, biomedicine, alternative/complementary medicine, consumer health and seventeen allied health disciplines. It also provides access to health care books, nursing dissertations, selected conference proceedings, standards of practice, audiovisuals and book chapters. Full-text journals, legal cases, clinical innovations, critical paths, research instruments and clinical trials are all included.
Emcare covers all nursing specialities and nursing healthcare professions. It includes international coverage of allied health, education and training, development and management, midwifery, health and healthcare economics, clinical medical and healthcare social work, psychiatry and mental health, and traumatology, emergency and critical care medicine.
Emcare vs CINAHL comparison (courtesy of Wolters Kluwer)
Emcare = 3,500 peer-reviewed journals vs CINAHL 1,380 peer reviewed journals
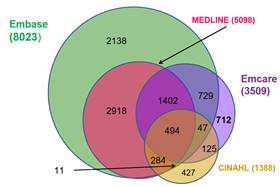
The 427 journals in CINAHL that are not covered by Medline, Emcare or Embase are what those databases consider to be low quality/magazine type/non-peer-reviewed titles.
If the search is on a nursing or allied health topic, CINAHL is a must, and Emcare should be covered for exhaustiveness.
If you ‘just’ want to cover the topic’s potential nursing aspect, searching Emcare only is enough.
When devising your search strategy remember: CINHAL uses MeSH, while Emcare uses Emtree for subject indexing.
We hope this helps but remember you can contact us on bsuhlibrary@nhs.net for further guidance.
Or book onto our Finding Quality Health Information course for an in-depth overview.

